近期,我们研究生武亚可、吴富英(通讯)、张刘挺(通讯)等的研究成果“Constructing a favorable microenvironment for robust hydrogen storage in MgH2 through synergistic cooperation with Mn and Mg2Ni”在《Rare Metals》(IF=11)上发表。
论文简介如下:
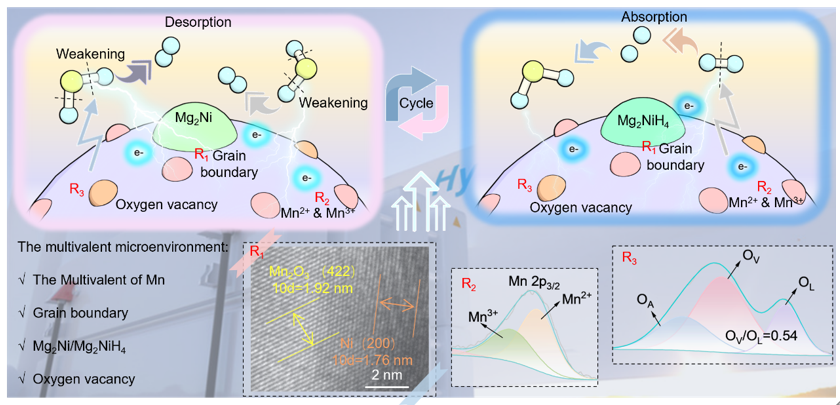
MgH2 is particularly noteworthy in metal solid-state hydrogen storage households due to its outstanding hydrogen storage capacity (7.6 wt%, 100g/L). Nevertheless, the pronounced electrostatic attraction between Mg2+ and H- stabilizes MgH2, trapping hydrogen in a low-energy configuration from which it is reluctant to escape. Weakening the electrostatic attraction between Mg2+ ions and H- ions in MgH2 is vital for improving the kinetic performance of MgH2 for hydrogen storage. Herein, a multivalent microenvironment is synergistically created by Mn and Mg2Ni to break the stable structure of MgH2, enabling rapid and stable de/hydrogenation performance. Specifically, the catalyzed MgH2 system rapidly emits 5.98 wt% H2 at 265 °C within just 20 min and swiftly absorbs 6.24 wt% H2 at 150 °C in a mere 10 min. Microscopic characterization shows that a tight interface is formed between Ni and Mn2O3, which provides a stable anchor point for the formation of hydrogen pumps. Additionally, the multivalency of Mn and abundant oxygen vacancies accelerate the electron transfer and provide the shortest path for H dissociation. Moreover, Density functional theory (DFT) indicates that Mg-H is extracted from 0.173 to 0.204 nm after modification, achieving a reduced decomposition energy of MgH2. Besides, 97.8% reversible hydrogen storage capacity was maintained after 30 cycles, presenting prominent potential for practical.