近期,我们教师张刘挺(第一作者,通讯)、研究生张佳雯(第二作者)、陈代芬(通讯)等的研究成果“Mn1.48Ti1.1V0.3Zr0.12 nano-pumps enhanced burst effect on solid-tate hydrogen storage in MgH2”在《International Journal of Hydrogen Energy》(IF=8.3)上发表。
论文简介如下:
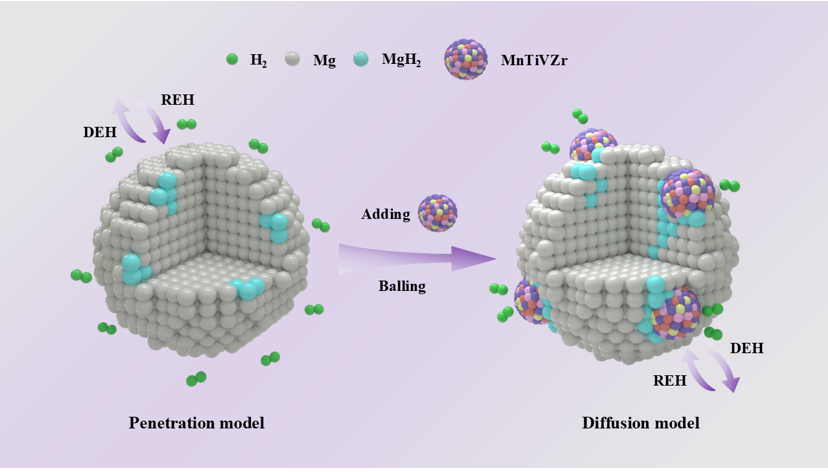
To optimize the hydrogen storage performance of magnesium hydride (MgH2), which is valued for its high capacity and abundance but suffers from slow de/hydrogenation kinetics, a strategic approach involving a high-performance catalyst is crucial. In this study, a Mn1.48Ti1.1V0.3Zr0.12 hydrogen storage alloy was chosen and processed into nanosheets to enhance MgH2's hydrogen storage capabilities. The MgH2 composite with MnTiVZr-4 nanosheets demonstrated dehydrogenation at a lower temperature of 196.9 ℃, with the activation energy for dehydrogenation significantly reduced to 92.6±4.8 kJ·mol-1. Besides, the composite showed rapid hydrogen absorption even at room temperature (25 ℃) and was capable of charging 5.2 wt% H2 in just 10 min at 150 ℃. Meanwhile, the composite maintained stable hydrogen absorption and desorption over 60 cycles, with a final capacity of 6.1 wt%, indicating robust cycling performance. The enhanced performance, combined with the excellent cycling stability, positions this optimized MgH2 composite as a promising material for practical hydrogen storage applications.